Guide to Diverticulitis Symptoms:
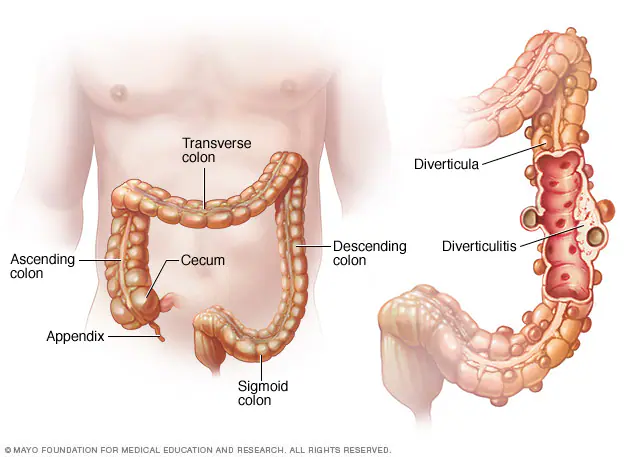
Table of Contents
Understanding Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation or infection of small pouches, known as diverticula, that can form in the walls of the digestive tract. These pouches are most commonly found in the colon. When these pouches become inflamed or infected, it leads to diverticulitis, a painful and potentially serious condition.
Symptoms
A common symptom of diverticulitis is pain in the area below the chest called the abdomen. Most often, pain is in the lower left abdomen.
Pain from diverticulitis is usually sudden and intense. Pain may be mild and gradually worsen, or the intensity of the pain may vary over time.
Other signs and symptoms of diverticulitis may include:
- Nausea.
- Fever.
- Tenderness in the abdomen when touched.
- Changes in stool, including sudden diarrhea or constipation.
Common Symptoms of Diverticulitis
Abdominal Pain
One of the most common and notable symptoms of diverticulitis is abdominal pain. This pain usually occurs in the lower left side of the abdomen. It can be sudden and severe, or it can start off mild and become progressively worse over several days.
Changes in Bowel Habits
Diverticulitis can cause significant changes in bowel habits. Patients may experience bouts of diarrhea or constipation. The changes can be unpredictable and cause considerable discomfort.
Fever and Chills
Fever and chills are common symptoms that indicate an infection in the body. When diverticulitis is present, these symptoms often accompany the abdominal pain and can indicate the severity of the inflammation or infection.
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are also frequently reported by those suffering from diverticulitis. These symptoms can exacerbate the discomfort and may also contribute to dehydration and further complications if not managed properly.
Bloating and Gas
Bloating and excess gas are common symptoms that can cause significant discomfort. These symptoms are often a result of the inflammation in the colon, leading to trapped gas and a feeling of fullness.
Complications of Diverticulitis
Abscess Formation
An abscess, which is a collection of pus, can form in the wall of the colon. This is a serious complication that can cause severe pain and requires immediate medical attention.
Perforation of the Colon
In severe cases, diverticulitis can lead to a perforation, or hole, in the colon. This can cause contents of the intestine to leak into the abdominal cavity, leading to a life-threatening infection known as peritonitis.
Fistula
A fistula is an abnormal connection that forms between two organs or between an organ and the skin. In the case of diverticulitis, a fistula can form between the colon and the bladder, small intestine, or skin. This requires surgical intervention to correct.
Intestinal Obstruction
Scar tissue from repeated bouts of diverticulitis can cause a blockage in the intestine, preventing the normal passage of stool and requiring surgical treatment to resolve.
Diagnosis of Diverticulitis
Medical History and Physical Examination
Diagnosis often begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. The doctor will ask about symptoms, duration, and severity, and perform an abdominal examination to check for tenderness and swelling.
Imaging Tests
- CT Scan: A CT scan is the most common imaging test used to diagnose diverticulitis. It can show the presence of inflamed or infected pouches, abscesses, and other complications.
- Ultrasound: In some cases, an abdominal ultrasound may be used, especially in younger patients or those for whom radiation exposure is a concern.
Laboratory Tests
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can reveal signs of infection or inflammation, such as an elevated white blood cell count.
- Stool Tests: Stool tests can help rule out other causes of gastrointestinal symptoms, such as infections or inflammatory bowel disease.
Treatment Options for Diverticulitis
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat the infection associated with diverticulitis. The type and duration of antibiotic treatment depend on the severity of the condition.
Dietary Changes
During an acute attack of diverticulitis, a clear liquid diet may be recommended to allow the colon to heal. Gradually, patients can return to a normal diet, but may need to avoid certain foods that can exacerbate symptoms.
Pain Management
Pain relief is an important aspect of treatment. Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen, may be used. In more severe cases, stronger prescription pain relievers may be necessary.
Surgery
Surgical intervention may be required in cases of recurrent diverticulitis or complications such as abscesses, fistulas, or intestinal obstruction. The type of surgery depends on the location and severity of the problem.
Preventive Measures for Diverticulitis
- Also Read :
- Walking Pneumonia Symptoms : What does it mean ?
- what are the advantages of having a healthy population
- Best Fitness Affiliate Programs
- Summer Healthy Dinner Ideas
- Self-care tips for Crohn’s disease
High-Fiber Diet
A diet high in fiber can help prevent the formation of diverticula and reduce the risk of diverticulitis. Fiber helps keep the bowel movements regular and prevents constipation, which can contribute to the formation of diverticula.
Hydration
Drinking plenty of fluids is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Adequate hydration helps keep stool soft and reduces the risk of constipation.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy digestive system and prevent constipation. Exercise helps stimulate the normal contractions of the intestines, which can prevent the formation of diverticula.
Avoiding Certain Foods
Some foods, such as nuts, seeds, and popcorn, have traditionally been thought to exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms. While recent studies suggest these foods may not increase the risk, it is still important for individuals to monitor their own symptoms and avoid foods that seem to trigger attacks.
Research and Advancements in Diverticulitis Treatment
Emerging Therapies
Research is ongoing to find more effective treatments for diverticulitis. Emerging therapies include:
- Probiotics: Studies are exploring the use of probiotics to maintain gut health and prevent diverticulitis flare-ups.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments based on individual genetic profiles is an area of active research, aiming to provide more effective and targeted therapies.
Surgical Innovations
Advancements in surgical techniques are improving outcomes for those requiring surgery for diverticulitis. Minimally invasive procedures, such as laparoscopic surgery, reduce recovery time and minimize complications.
Dietary Research
New research is continually enhancing our understanding of the relationship between diet and diverticulitis. This research is helping to refine dietary recommendations to prevent flare-ups and manage symptoms more effectively.
Conclusion
Diverticulitis is a manageable condition with the right approach to diet, lifestyle, and medical care. By understanding the symptoms, seeking appropriate treatment, and making proactive lifestyle changes, individuals can lead a healthy, fulfilling life despite having diverticulitis.
Adopting a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding trigger foods are key preventive measures. Regular medical check-ups and staying informed about the latest research and advancements in treatment options can further enhance the management of this condition.
By leveraging support systems and taking advantage of emerging therapies and surgical innovations, those with diverticulitis can significantly improve their quality of life. Ongoing research continues to provide hope for even better management and treatment options in the future.
What is diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis is the inflammation or infection of small pouches called diverticula that can form in the walls of the digestive tract, most commonly in the colon. When these pouches become inflamed or infected, it leads to diverticulitis, causing pain and other symptoms.
What are the common symptoms of diverticulitis?
Common symptoms include:
Abdominal pain, usually on the lower left side
Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea or constipation)
Fever and chills
Nausea and vomiting
Bloating and gas
How is diverticulitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves:
Medical history and physical examination
Imaging tests such as a CT scan or ultrasound
Blood tests to check for signs of infection or inflammation
Stool tests to rule out other gastrointestinal issues
What causes diverticulitis?
The exact cause of diverticulitis is not known, but it is believed to be related to:
Low-fiber diet leading to constipation and increased pressure in the colon
Aging, which can weaken the walls of the colon
Genetic factors
